Find a Top Rated IT Security Near You
- Trusted by +502,727 customers
- 100% verified ratings
- Absolutely free to use








How It Works
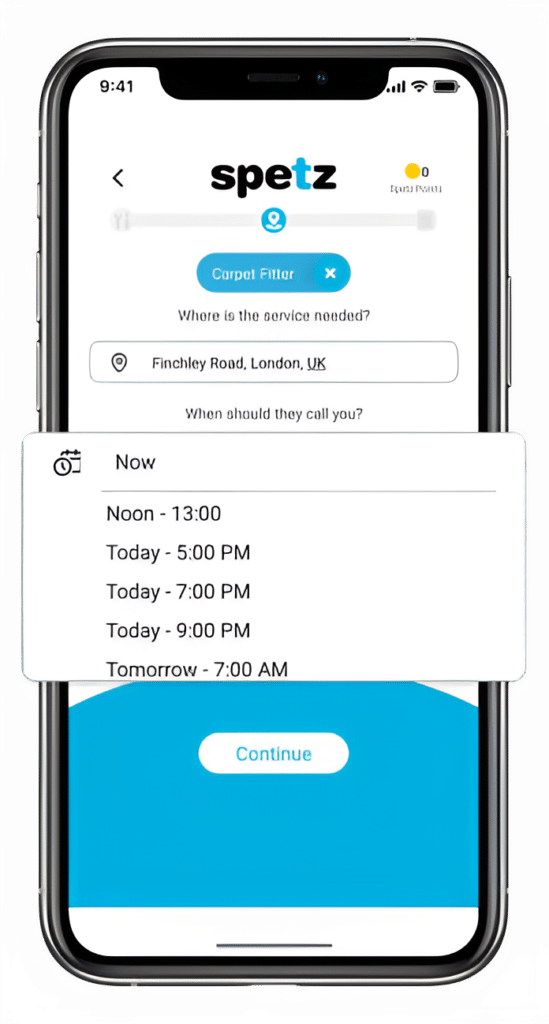
Make your free request
Simply enter the service you need, and your details then press "Spetz-it".
Get the job done
You'll be connected immediately to a nearby top-rated service provider.
Rate your specialist
Your rating is important. So you can help other customers get the best specialist too.
IT Security
Frequently Asked Questions
Hiring the best IT Security professional or firm near you requires a comprehensive approach, considering the nuances and rapidly evolving nature of the cybersecurity industry. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
1. Define Your Needs:
– Identify the specific security needs of your organization. Are you looking for vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, network security, endpoint security, cloud security, compliance management, incident response, or a combination of these?
2. Research and Gather Recommendations:
– Seek recommendations from industry peers, IT professionals within your network, or local business organizations.
– Search online for IT security professionals or firms in your area, and review their ratings, feedback, and customer testimonials.
– Consider industry-specific forums, cybersecurity conferences, or local IT events to find potential candidates.
3. Check Qualifications and Certifications:
– Ensure potential candidates have relevant certifications, such as CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional), CISM (Certified Information Security Manager), CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker), or CompTIA Security+.
– Ask about their education, training, and ongoing professional development to ensure they stay updated with the latest threats and security practices.
4. Experience and Expertise:
– Look for professionals or firms with experience relevant to your industry. For example, if you’re in healthcare, it would be beneficial to have someone familiar with HIPAA compliance.
– Ask about the size and types of organizations they’ve worked with. If you’re a small business, ensure they have experience with similar-sized businesses.
5. Initial Consultation:
– Arrange a meeting (either in-person or virtual) to discuss your needs and concerns.
– Use this opportunity to gauge their communication skills, understanding of your industry, and their approach to IT security.
6. Ask for References:
– Request case studies or references from previous clients, especially from projects similar to what you’re seeking.
– Contact these references to inquire about their experiences, outcomes, and any challenges faced.
7. Scope of Work and Pricing:
– Get a detailed proposal outlining the scope of work, deliverables, timelines, and costs.
– Ensure there are no hidden fees and that the proposal aligns with your budget.
8. Tools and Technologies:
– Inquire about the tools, software, and methodologies they use. Ensure they utilize industry-recognized and up-to-date technologies.
– If they’re using proprietary tools, ask for demonstrations or explanations of how these tools can benefit your organization.
9. Response Times and Availability:
– Check their availability for emergencies. Cybersecurity incidents can occur outside regular business hours, so having 24/7 support might be crucial.
– Ask about their incident response time and processes.
10. Contract and Terms:
– Review any contractual terms, ensuring there’s clarity on responsibilities, deliverables, and any service level agreements (SLAs).
– Consider involving legal counsel to review the terms, especially concerning data handling, confidentiality, and non-disclosure agreements.
11. Regular Reviews:
– IT security is an ongoing process. Schedule regular check-ins or reviews with your chosen professional or firm to discuss any updates, threats, or changes in the IT landscape.
12. Stay Updated:
– Encourage continuous learning and training for both your team and the IT security professional or firm you hire. The cybersecurity landscape is dynamic, and staying updated is crucial.
Remember, while certifications and technical skills are crucial, communication, trustworthiness, and understanding of your industry and organization are equally vital when hiring an IT security professional.
IT security, often referred to as cybersecurity, involves the practice of protecting information systems from theft, damage, disruption, or unauthorized access to the hardware, software, and the information they contain, as well as from disruption or misdirection of the services they offer. Given the increasing number of cyber threats, the importance of IT security has grown exponentially in recent years.
What IT Security Involves:
1. Protecting Information: This involves safeguarding databases, websites, and computer systems from unauthorized access which could lead to data theft or damage.
2. Preventing Disruption: Ensuring services provided by information systems run without interruption, e.g., Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack prevention.
3. Risk Management: Identifying, evaluating, and implementing strategies to manage and mitigate risks.
4. Compliance: Ensuring systems adhere to regulations and standards, especially in industries like finance and healthcare.
5. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning: Planning for potential security incidents or disasters to ensure business operations can continue with minimal disruption.
Key Tasks of an IT Security Professional:
1. Vulnerability Assessments: Identifying, quantifying, and prioritizing vulnerabilities in systems.
2. Penetration Testing: Simulating cyberattacks to find vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them.
3. Implementing Security Protocols: This can include setting up firewalls, configuring VPNs, implementing multi-factor authentication, and more.
4. Incident Response: Reacting to security breaches or other incidents, investigating their causes, and taking steps to prevent future occurrences.
5. Security Monitoring: Keeping an eye on systems and networks for any signs of breaches or unauthorized activities.
6. User Training: Educating employees about best practices to avoid security threats, such as phishing scams.
7. Staying Updated: The world of IT security is always evolving. Professionals need to stay updated with the latest threats and security measures.
8. Secure Coding: For those involved in application security, ensuring that software is coded without vulnerabilities is essential.
9. Policy Development: Creating and implementing security policies and procedures that set the standard for organizational practices.
10. Physical Security Measures: Implementing measures to protect physical devices and hardware.
Technologies and Tools:
IT security professionals utilize various technologies and tools, including but not limited to:
– Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
– Firewalls
– Anti-virus and anti-malware software
– Encryption tools
– VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
– SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems
Benefits of IT Security:
– Protects Sensitive Data: Prevents unauthorized access and potential theft of information.
– Ensures Business Continuity: Minimizes disruptions due to security incidents.
– Builds Trust: Clients and customers are more likely to trust organizations that prioritize data protection.
– Compliance: Helps businesses stay compliant with industry regulations and avoid potential legal repercussions.
Given its importance, IT security is a broad and multifaceted domain, with professionals often specializing in specific areas, such as network security, application security, endpoint security, cloud security, or compliance.
An IT security professional, often referred to as a cybersecurity specialist, can cover a wide array of roles and responsibilities within the domain of information security. The specific job roles and tasks they can assist with include:
1. Security Analyst:
– Monitors network traffic and activity to identify suspicious behavior.
– Analyzes vulnerabilities and recommends protective measures.
2. Penetration Tester or Ethical Hacker:
– Simulates cyber-attacks on systems, networks, and applications to identify vulnerabilities before malicious entities can exploit them.
– Recommends and sometimes implements solutions to fix discovered vulnerabilities.
3. Security Consultant:
– Provides expert advice to organizations on how to best protect their IT assets.
– Conducts security assessments and recommends strategies to improve security posture.
4. Security Engineer/Architect:
– Designs and implements secure network solutions to defend against advanced cyber threats.
– Develops and creates security infrastructure for organizations.
5. Incident Responder:
– Acts swiftly during a security breach to contain and mitigate its effects.
– Investigates the cause of the breach and works on preventing future incidents.
6. Security Administrator:
– Manages and administers security tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and anti-virus software.
– Maintains security policies and ensures organizational compliance.
7. Cryptographer/Cryptanalyst:
– Develops encryption systems to protect sensitive data.
– Analyzes and decrypts hidden information in cryptographic security systems.
8. Security Software Developer:
– Designs and develops software with security built-in from the ground up.
– Patches software vulnerabilities and creates security updates.
9. Chief Information Security Officer (CISO):
– Senior-level executive responsible for developing and implementing an organization’s information security program.
– Oversees the security team and coordinates security efforts across the organization.
10. Forensic Computer Analyst:
– Investigates cybercrimes by analyzing computer systems and retrieving evidence.
– Works closely with law enforcement agencies in cybercrime cases.
11. Security Auditor:
– Evaluates and assesses the effectiveness of an organization’s security measures.
– Provides reports and suggestions for improvements based on audits.
12. Security Researcher:
– Investigates new and emerging threats in the cybersecurity landscape.
– Publishes research, often helping software and hardware vendors patch vulnerabilities.
13. Security Sales Engineer:
– Works for security product vendors, demonstrating products to potential clients.
– Assists in tailoring security solutions to fit the specific needs of businesses.
14. Security Trainer/Educator:
– Educates staff and other stakeholders about security best practices.
– Conducts security awareness training sessions.
15. Compliance Analyst:
– Ensures that security practices comply with external regulations and standards.
– Assists organizations in preparing for and passing security compliance audits.
16. Vulnerability Assessor:
– Conducts assessments to discover security weaknesses in an organization’s infrastructure.
– Provides detailed reports and mitigation strategies.
Each of these roles has a specific focus, but they all contribute to the overall goal of safeguarding an organization’s digital assets and infrastructure. Depending on the size and type of an organization, an IT security professional may wear multiple hats or specialize in just one of these areas.
The cost of IT security services in Australia varies widely based on several factors: the nature of the service, the complexity of your IT environment, the expertise of the service provider, the location of the service (whether it’s in a metropolitan area or regional area), and more.
To give you a ballpark figure:
1. Hourly Rate for IT Security Consultants: Depending on their expertise and reputation, IT security consultants in Australia can charge anywhere from AUD 70 to AUD 300+ per hour. Senior consultants or those with specialized skills may charge even more.
2. Penetration Testing: A standard penetration test can range from AUD 3,000 to AUD 20,000 or more, depending on the scope of the test. For example, testing a small website would be on the lower end, while a comprehensive test of a large organization’s entire IT infrastructure would be on the higher end.
3. Security Audits: Basic security audits can start from AUD 5,000 and can go up to AUD 50,000+ for larger enterprises with complex networks.
4. Managed Security Services: For businesses that outsource their IT security functions to a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP), costs can range from AUD 1,000 to AUD 10,000+ per month based on the breadth of services provided.
5. Incident Response: If you’re hiring a professional to respond to a security incident, the costs can be unpredictable and depend on the nature and extent of the breach. This can range from a few thousand dollars for smaller incidents to hundreds of thousands for major breaches.
6. Salaries for In-House IT Security Professionals: If you’re considering hiring an in-house IT security professional:
– A junior IT security analyst might have a salary ranging from AUD 60,000 to AUD 90,000 annually.
– A senior IT security expert or CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) can command salaries from AUD 120,000 to AUD 250,000 or more.
7. Software & Tools: Subscription costs for security software and tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint security solutions, vary based on the product and the scale of deployment.
Remember, these are rough estimates, and prices can vary based on many factors. It’s essential to get multiple quotes from service providers and evaluate the cost versus the value they provide. Given the importance of cybersecurity and the potential costs of a security breach, it’s often wise to view IT security spending as a crucial investment rather than just an expense.
When considering hiring an IT security professional or firm, it’s essential to ask the right questions to ensure you’re getting a qualified and experienced provider. Here’s a list of questions you might consider asking:
1. Qualifications & Experience:
– What certifications do you hold? (Look for certifications like CISSP, CEH, CISM, CompTIA Security+, etc.)
– How many years of experience do you have in IT security?
– Can you provide references or case studies from previous clients or projects?
2. Services Offered:
– What specific security services do you offer (e.g., penetration testing, security audits, managed security services)?
– Do you have expertise in a particular industry or type of business?
– How do you stay updated with the latest threats and security measures?
3. Incident Response:
– How do you handle security incidents or breaches?
– What is your response time in case of an emergency?
– Do you offer 24/7 monitoring and support?
4. Tools & Technologies:
– What tools, technologies, or methodologies do you typically use in your work?
– How do you ensure that the tools and software you use are up-to-date?
5. Reporting & Communication:
– How often will you provide reports or updates?
– What will be included in the reports? (Look for details on vulnerabilities found, recommended actions, and other insights.)
– What’s your communication protocol for regular updates and emergencies?
6. Pricing & Contract:
– How do you structure your pricing? Is it per project, hourly, or a monthly retainer?
– Are there any additional costs or fees that I should be aware of?
– What’s the duration of the contract or agreement, and what are the terms for renewal or termination?
7. Data Privacy:
– How do you ensure the privacy of our data during and after security assessments?
– Do you have a privacy policy in place, and can you share it with us?
8. Insurance:
– Do you have professional liability or cybersecurity insurance? If so, what does it cover and up to what amount?
9. Local Regulations & Compliance:
– Are you familiar with local regulations and compliance standards relevant to our industry?
– How do you ensure your services will help us stay compliant with these regulations?
10. Team & Resources:
– Who will be working on our project? Can you provide details on their experience and qualifications?
– If you’re a larger firm, will we have a dedicated point of contact or account manager?
11. Physical Security:
– If our project involves on-site work, how do you ensure the physical security of our premises?
12. Continuous Learning:
– How do you and your team keep your skills up-to-date? Do you engage in ongoing training or attend industry conferences?
Lastly, always trust your instincts. If you feel uncertain about a provider, even if their answers seem satisfactory, it may be a good idea to continue your search. Cybersecurity is critical, and it’s essential to partner with someone you trust implicitly.